-
Products
 Horus Visual & Laser
Horus Visual & Laser
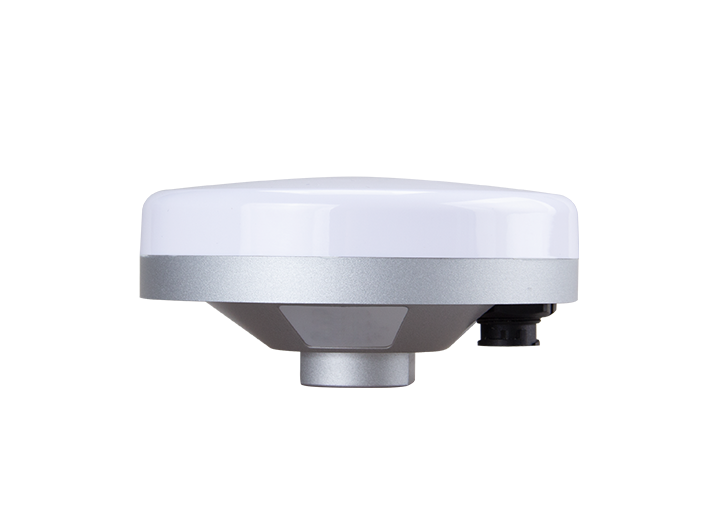
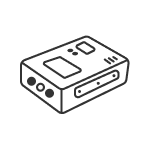
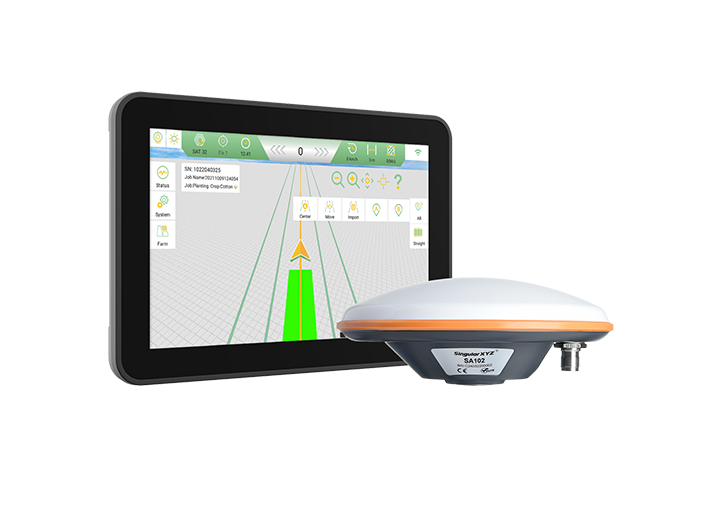
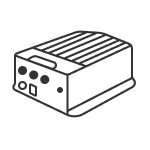
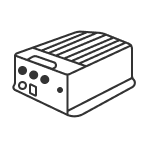
GNSS Receiver Orion ONE
Orion ONE
GNSS Receiver Orion ONE
Orion ONE
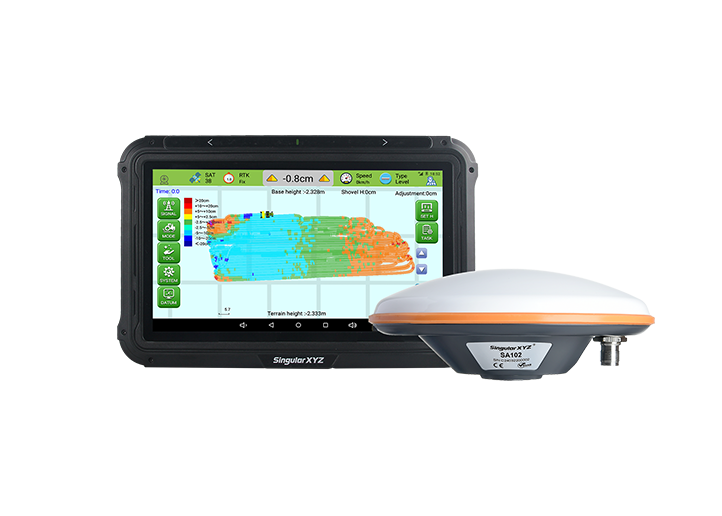
Laser GNSS Receiver Orion ONE
Orion ONE
AR GNSS Receiver X1 GNSS Receiver
X1 GNSS Receiver X1 Pro GNSS Receiver
X1 Pro GNSS Receiver X1 Lite GNSS Receiver
X1 Lite GNSS Receiver Xbase
Xbase
GNSS Receiver Z1 GNSS Receiver
Z1 GNSS Receiver Z1 Lite GNSS Receiver
Z1 Lite GNSS Receiver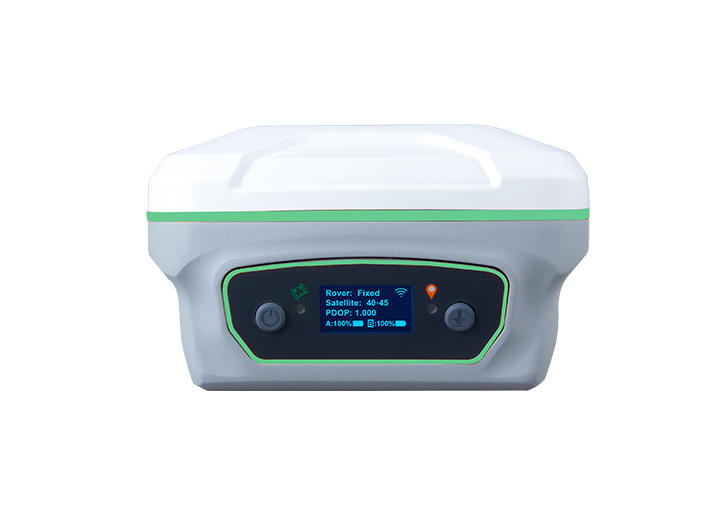 Y1 GNSS Receiver
Y1 GNSS Receiver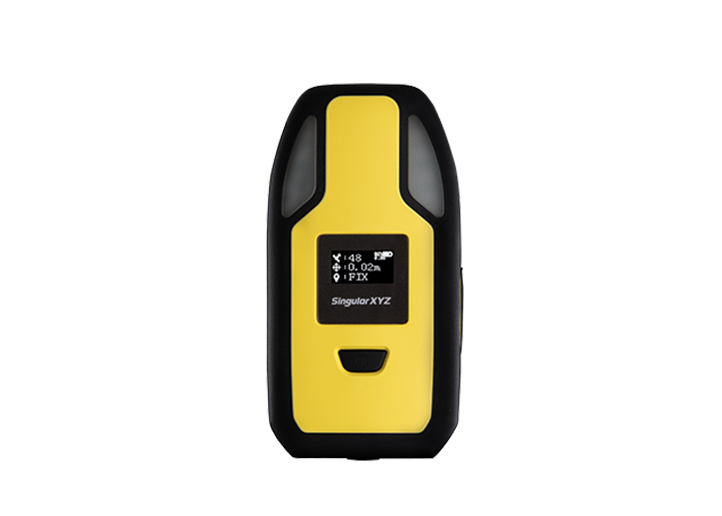 P2 Plus GNSS Receiver
P2 Plus GNSS Receiver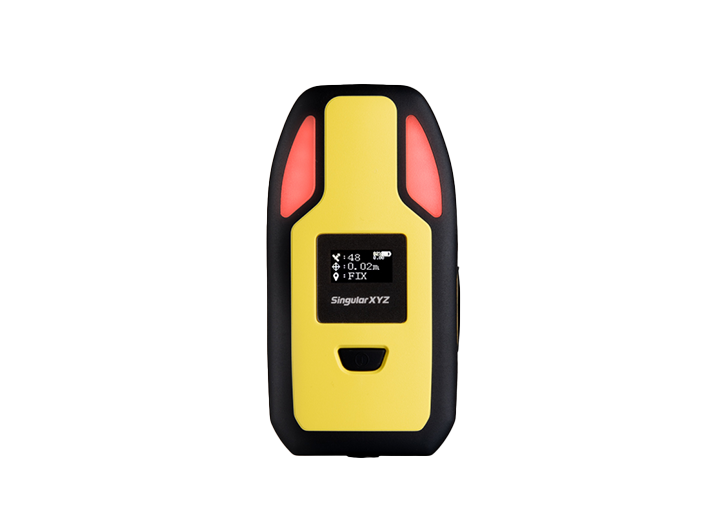 P2 GNSS Receiver
P2 GNSS Receiver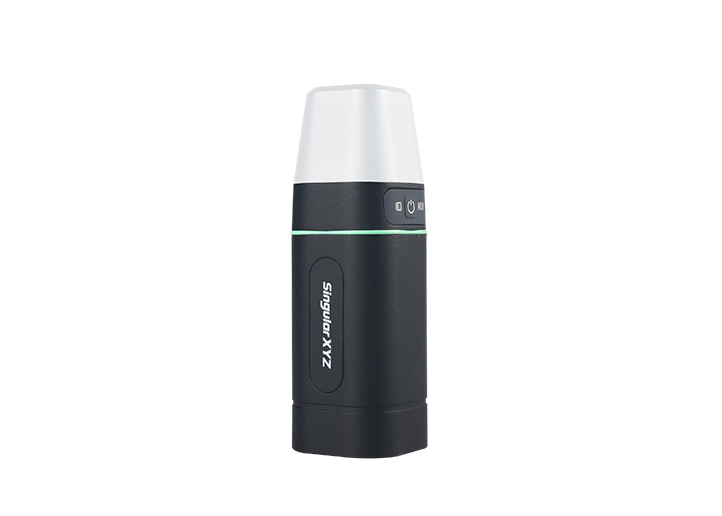 Sfaira ONE Plus GNSS Receiver
Sfaira ONE Plus GNSS Receiver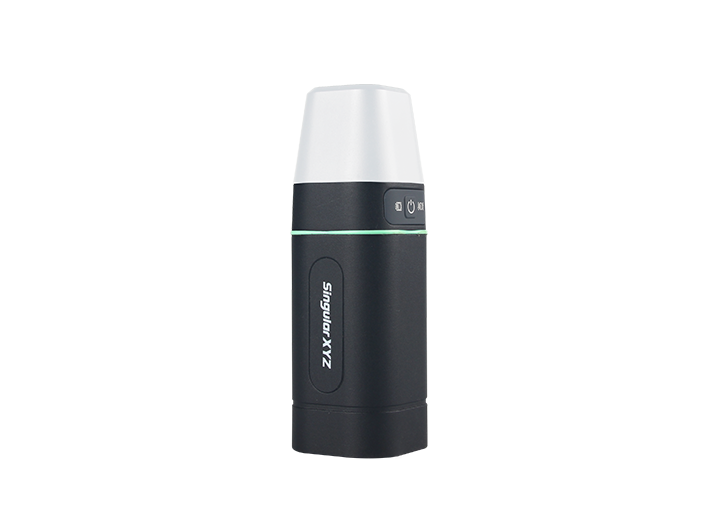 Sfaira ONE GNSS Receiver
Sfaira ONE GNSS Receiver -
Solutions
- Support
- Blog & FAQ
- About Us
- Talk to Sales















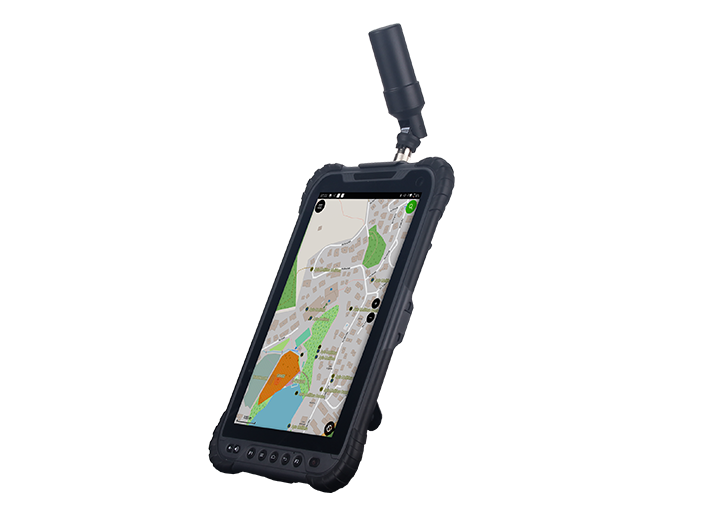





















































































 Home
Home